Comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), often referred to simply as the Dow, is one of the most renowned stock market indices globally. Investors, analysts, and financial enthusiasts frequently compare the Dow Jones Industrial Average to other major indices to gauge its performance and understand broader market trends. This comprehensive guide will delve into various aspects of the DJIA, from its historical context to its contemporary relevance, and provide a detailed comparison with other leading stock indices.
What is the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, commonly known as the DJIA, is a stock market index that measures the performance of 30 significant publicly traded companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It serves as a barometer for the overall health of the U.S. stock market and is one of the most frequently referenced indices when comparing market performance.
Historical Overview of the Dow Jones Industrial Average
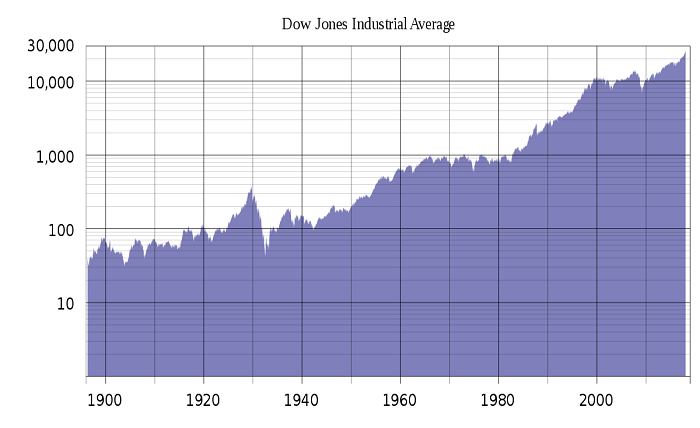
The Dow Jones Industrial Average was created by Charles Dow, co-founder of Dow Jones & Company, and Edward Jones in 1896. Initially, the DJIA included 12 industrial companies, reflecting the dominance of the industrial sector in the American economy. Over the years, the composition of the Dow Jones Industrial Average has evolved, incorporating companies from various sectors to better represent the modern economy. Comparing the historical milestones of the Dow Jones Industrial Average with other indices highlights its longstanding influence in the financial world.
Composition of the Dow Jones Industrial Average
Unlike many other indices, the Dow Jones Industrial Average is price-weighted, meaning that companies with higher stock prices have a more significant impact on the index’s movement. The current 30 companies included in the Dow Jones Industrial Average span various industries, including technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods. Comparing the sectoral representation of the Dow Jones Industrial Average with indices like the S&P 500 reveals differences in market weighting and composition.
Methodology Behind the Dow Jones Industrial Average
The methodology for calculating the Dow Jones Industrial Average is relatively straightforward but unique. The DJIA is calculated by summing the prices of its 30 component stocks and dividing the total by a divisor, which adjusts for stock splits and other corporate actions. This price-weighted method contrasts with the market capitalization-weighted methods used by indices like the S&P 500, providing a distinct perspective when comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average to other indices.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average vs. S&P 500
When comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average with the S&P 500, several key differences emerge. The S&P 500 includes 500 of the largest U.S. companies and is market capitalization-weighted, offering a broader and more comprehensive view of the market. Despite these differences, both indices often move in tandem, reflecting similar market trends. However, the Dow Jones Industrial Average can sometimes show different short-term movements due to its price-weighted nature and smaller number of components.
Comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average with NASDAQ
The NASDAQ Composite Index primarily includes technology companies and is market capitalization-weighted. Comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average with the NASDAQ highlights the DJIA’s broader industry representation versus NASDAQ’s tech-heavy focus. This comparison is particularly relevant during periods of significant technological advancements or market volatility, where the NASDAQ may experience more pronounced movements compared to the more diversified Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Global Indices: How Does the Dow Jones Industrial Average Stack Up?
Comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average with global indices like the FTSE 100, Nikkei 225, and DAX provides insight into how U.S. markets fare against international counterparts. The DJIA’s performance often reflects broader economic trends and geopolitical events, influencing and being influenced by global markets. Understanding these comparisons can help investors gauge the relative strength and stability of the U.S. market compared to other major economies.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average in Economic Crises
Historical analysis of the Dow Jones Industrial Average during economic crises, such as the Great Depression, the 2008 financial crisis, and the COVID-19 pandemic, offers valuable lessons. Comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average’s resilience and recovery during these periods with other indices can provide insights into market behavior and investor sentiment during times of economic stress. The DJIA often serves as a benchmark for economic recovery and investor confidence.
Future Trends and Predictions for the Dow Jones Industrial Average
Forecasting future trends for the Dow Jones Industrial Average involves analyzing economic indicators, corporate earnings, and global events. Comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average’s predicted trajectory with other indices can help investors make informed decisions. While past performance is not indicative of future results, understanding historical patterns and current market conditions can provide valuable context for predicting the DJIA’s future movements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Dow Jones Industrial Average remains a critical indicator of the U.S. stock market and the broader economy. By comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average with other major indices like the S&P 500, NASDAQ, and global benchmarks, investors can gain a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. The DJIA’s unique composition and methodology provide distinct insights, making it an essential tool for investors and analysts alike.
FAQs
1. What is the primary difference between the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500?
- The Dow Jones Industrial Average is a price-weighted index of 30 significant companies, while the S&P 500 is a market capitalization-weighted index of 500 large companies, providing a broader market view.
2. Why is the Dow Jones Industrial Average price-weighted?
- The Dow Jones Industrial Average is price-weighted to reflect the influence of stock price movements of its components, a methodology chosen by its creators to provide a straightforward calculation approach.
3. How does the Dow Jones Industrial Average impact the global market?
- The Dow Jones Industrial Average often influences global markets as it reflects the health of the U.S. economy, with movements in the DJIA potentially affecting investor sentiment worldwide.
4. Can the Dow Jones Industrial Average be considered a good investment benchmark?
- Yes, the Dow Jones Industrial Average is widely regarded as a reliable benchmark for the U.S. stock market, helping investors gauge overall market performance and make informed investment decisions.
5. What sectors are most represented in the Dow Jones Industrial Average?
- The Dow Jones Industrial Average includes companies from various sectors, with significant representation from technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods, providing a diversified market snapshot.