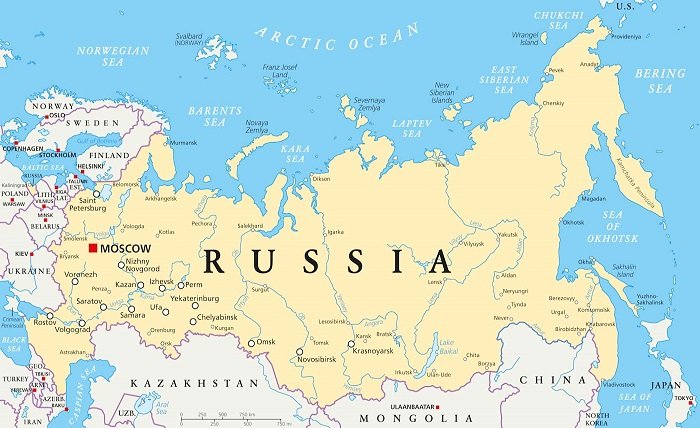
Russia, the largest country in the world, spans across Eastern Europe and northern Asia. This blog post delves into the diverse geographical regions of Russia, using the Russia map to highlight key features, cities, and natural landmarks. From the frozen tundras of Siberia to the bustling streets of Moscow, we explore what makes Russia a giant in every sense of the word.
The Political Divisions of Russia
The Russia map reveals not just the vast size of the nation but also its complex political divisions. Russia is divided into 85 federal subjects, including oblasts, republics, krais, autonomous okrugs, and two federal cities — Moscow and St. Petersburg. Each region has its own government and contributes uniquely to the national identity and governance.
Major Cities and Urban Centers
Moscow, the capital, is prominently visible on any Russia map. As the economic and political heart of Russia, Moscow is surrounded by major urban centers like Saint Petersburg, Novosibirsk, and Yekaterinburg. These cities are not just population centers but also cultural and economic hubs.
Russia’s Vast Road and Railway Networks
Transportation in such a vast country is a challenge. The Russia map shows an extensive network of roads and railways that link the remote areas of Siberia to the more populous west. The Trans-Siberian Railway, stretching from Moscow to Vladivostok, is a key feature of this network.
The Russian Relief: Mountains and Plains
Russia’s topography is varied. The Ural Mountains divide Europe and Asia, offering rich mineral resources. Siberia’s plains and Eastern Russia’s volcanic regions are also prominent, providing Russia with its diverse landscapes and resources.
The Climate Zones of Russia
The Russia map is a climatic patchwork, ranging from arctic in Siberia to continental in the plains and temperate along the southern border. This diversity affects everything from living conditions to economic activities, particularly agriculture and resource extraction.
Key Rivers and Water Bodies
Major rivers like the Volga, the longest in Europe, and the Yenisei in Siberia, are crucial for transportation, water supply, and energy. The Caspian Sea, the world’s largest inland body of water, is also an important geographical feature noted on the Russia map.
Natural Resources and Mining Regions
Russia is rich in natural resources. The map highlights significant mining areas in the Ural Mountains, Siberian coal fields, and the oil-rich regions of Western Siberia, pivotal to Russia’s economy and global energy markets.
Protected Areas and National Parks
Russia’s commitment to conservation is evident in its many protected areas and national parks, such as the famous Lake Baikal and the volcanoes of Kamchatka. These regions are not only vital for biodiversity but also for scientific research and ecotourism.
The Arctic Expansion
Russia’s northern territories, prominently visible on the Russia map, are critical due to their geopolitical significance and the melting Arctic ice, opening new maritime routes and access to untapped resources.
Cultural Regions: From West to East
The cultural diversity of Russia is immense, with the European west differing greatly from the Asiatic east. The Russia map helps in understanding the cultural, linguistic, and ethnic diversities that are spread across the vast country.
Challenges of Environmental Conservation
Environmental conservation in Russia is a daunting task due to its size and industrial activities. Issues like pollution in the Volga River and deforestation in Siberia are critical challenges highlighted in discussions about Russia’s geography.
Future Prospects: Development and Challenges
Looking ahead, Russia faces both opportunities and challenges. Developing remote regions, managing environmental changes, and improving the quality of life for its diverse populations are ongoing tasks that the Russia map helps to contextualize.
Conclusion
The Russia map is more than a geographical tool; it is a window into the nation’s soul, showing its vastness, diversity, and complexity. Understanding Russia through its geography offers insights into its past, present, and future challenges and opportunities.
Looking for a reliable and secure crypto wallet? ecryptobit.com wallets offer advanced security features, user-friendly interfaces, and support for multiple cryptocurrencies. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, ecryptobit.com ensures your digital assets are protected and easily accessible. With fast transactions, real-time tracking, and top-notch encryption, these wallets are perfect for managing your crypto portfolio efficiently. ecryptobit.com wallets combine innovation with security, making them a top choice in the crypto space. Start your journey in the digital economy with confidence using ecryptobit.com’s trusted wallet solutions.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of the Ural Mountains in Russia?
- The Ural Mountains are significant as they mark the boundary between Europe and Asia and are rich in minerals and resources.
2. How does the climate affect life in Russia?
- Russia’s diverse climates affect everything from agriculture to lifestyle, with harsh winters and varied growing seasons influencing economic activities.
3. What are some major natural resources found in Russia?
- Russia is rich in oil, natural gas, coal, and precious metals, which are pivotal to its economy and global energy supplies.
4. Why are the Arctic territories increasingly important for Russia?
- The Arctic territories are becoming more important due to potential new shipping routes and access to natural resources as Arctic ice melts.
5. What challenges does Russia face in terms of environmental conservation?
- Major challenges include tackling industrial pollution, managing vast forest areas, and protecting endangered species and habitats.