Dow Jones Industrial Average Compare: Analyzing Market Trends
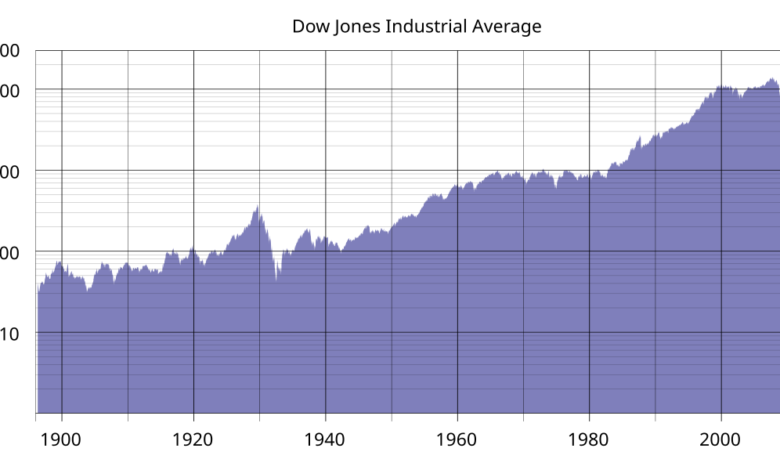
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a key stock market index. It includes 30 major U.S. Companies.
Comparing the DJIA to other indices helps investors understand market trends better. Understanding how the DJIA performs against other indices can guide investment decisions. It shows how different sectors and companies fare in the market. For new and seasoned investors, such comparisons offer valuable insights.
They reveal the strengths and weaknesses of various market segments. This blog will explore the DJIA in detail and compare it with other popular indices. By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of its role and significance in the financial world. This will help you make more informed investment choices.
Introduction To Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), often known simply as the Dow, stands as a cornerstone in the financial world. This iconic stock market index offers a snapshot of how some of the largest and most influential companies in the United States are performing.
History And Purpose
The DJIA was founded in 1896 by Charles Dow and Edward Jones. They aimed to create a benchmark to gauge the health of the American economy. Initially, the index included just 12 companies, mainly from the industrial sector.
Its purpose is clear: to provide a reliable indicator of the overall market performance. Over the years, the DJIA has evolved, reflecting changes in the economy and industry. Today, it includes 30 prominent companies across various sectors.
Key Components
These 30 companies are not fixed. They change as the economy shifts. The committee overseeing the DJIA selects companies based on their sustained growth and impact on the market.
Add more companies as needed
| Company | Industry |
|---|---|
| Apple Inc. | Technology |
| Boeing | Aerospace |
| Coca-Cola | Consumer Goods |
Each company in the DJIA has a significant role in its sector. They are leaders in their industries, and their performance impacts the overall index.
The DJIA is a price-weighted index, meaning companies with higher stock prices have a greater influence on the index’s movements. This unique structure sets it apart from other indices.
Understanding the DJIA helps investors gain insights into market trends. It serves as a barometer for the economic climate. Whether you are new to investing or an experienced trader, the DJIA offers valuable information.

Credit: www.wallstreetprep.com
Analyzing Market Trends
Understanding the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) requires a deep dive into market trends. Trends help investors predict future movements. This section will explore both short-term and long-term trends. These insights can guide investment strategies.
Short-term Trends
Short-term trends in the DJIA are often influenced by daily market news. Events like earnings reports, economic data, and geopolitical events can cause rapid changes. Investors use these trends for quick gains.
- Daily News: News impacts stocks quickly.
- Earnings Reports: Company performance drives stock prices.
- Geopolitical Events: Events affect market stability.
Technical analysis tools help identify these trends. Moving averages and Relative Strength Index (RSI) are popular tools. They show whether a stock is overbought or oversold. This helps in making buy or sell decisions.
Long-term Trends
Long-term trends in the DJIA reflect broader economic cycles. These trends span years or even decades. They are less affected by daily news.
- Economic Cycles: Periods of growth and recession.
- Market Sentiment: Overall investor confidence.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations drive long-term growth.
Fundamental analysis is key for long-term trends. Analysts look at company fundamentals like earnings, debt, and market position. This helps in understanding a company’s long-term potential.
Historical data is also crucial. It shows how the DJIA responded to past events. This can provide clues for future trends.
| Factor | Short-term Trend | Long-term Trend |
|---|---|---|
| News Impact | High | Low |
| Technical Analysis | Essential | Less Important |
| Fundamental Analysis | Less Important | Essential |
| Historical Data | Limited Use | Crucial |
Investors should balance both short-term and long-term trends. This holistic approach can lead to more informed decisions.
Comparing Market Indices
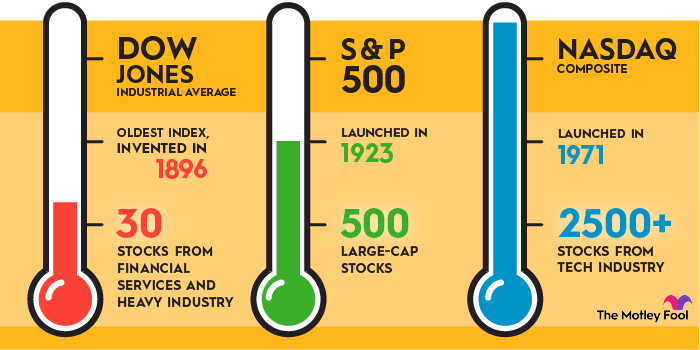
Investors often compare market indices to gauge the health of the economy. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), S&P 500, and NASDAQ are three major indices. Each one offers unique insights into market performance. Understanding their differences helps investors make informed decisions.
Dow Jones Vs. S&p 500
The Dow Jones includes 30 large U.S. companies. It focuses on blue-chip stocks. These companies are leaders in their industries. The S&P 500, on the other hand, includes 500 companies. It provides a broader market view. The Dow is price-weighted. The S&P 500 is market cap-weighted. This means that larger companies have more influence on the S&P 500.
Both indices are important. The Dow shows the performance of established companies. The S&P 500 reflects the overall market. Investors often use both to get a complete picture.
Dow Jones Vs. Nasdaq
The NASDAQ index includes over 3,000 companies. It has a heavy focus on technology stocks. The Dow Jones has fewer companies, with a mix of sectors. The NASDAQ is market cap-weighted. The Dow is price-weighted.
Tech stocks drive the NASDAQ. This makes it more volatile. The Dow is more stable, with a mix of industries. Investors looking at tech trends often follow the NASDAQ. Those interested in a broader view turn to the Dow.
Both indices offer valuable insights. Understanding their focus helps in making better investment choices.
Economic Indicators
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) serves as a key benchmark in the financial world. Investors and analysts rely on it to gauge the health of the stock market. Economic indicators play a significant role in influencing the DJIA. These indicators provide insights into the overall economy, helping to predict market trends.
Gdp Impact
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures a country’s economic performance. High GDP growth often leads to a rise in the DJIA. Investors feel confident, leading to increased investments. Conversely, low GDP growth can cause the DJIA to drop. It signals economic slowdown, making investors cautious.
Employment Rates
Employment rates directly affect the DJIA. High employment rates indicate a strong economy. More people with jobs mean higher consumer spending. This boosts company profits, positively impacting the DJIA. Low employment rates have the opposite effect. Fewer jobs mean less spending and lower company earnings, leading to a drop in the DJIA.
Sector Performance
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a vital indicator of the stock market’s health. It includes 30 major companies from various sectors. Analyzing sector performance within the DJIA can reveal trends and opportunities. This section dives into the performance of the technology and financial sectors.
Technology Sector
The technology sector has seen remarkable growth in recent years. Companies like Apple and Microsoft are key players. They have driven significant gains in the DJIA. The sector’s innovation and rapid growth often lead to higher stock prices. Here’s a brief overview:
| Company | Stock Price (2023) | YTD Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | $170 | +25% |
| Microsoft | $310 | +30% |
- Apple’s new products boost its stock price.
- Microsoft benefits from cloud computing growth.
Financial Sector
The financial sector is another crucial part of the DJIA. Banks like JPMorgan Chase and Goldman Sachs play a significant role. Their performance often mirrors the economy’s health. During economic growth, these stocks generally perform well. Here’s a snapshot:
| Company | Stock Price (2023) | YTD Growth |
|---|---|---|
| JPMorgan Chase | $150 | +15% |
| Goldman Sachs | $350 | +10% |
- JPMorgan Chase benefits from higher interest rates.
- Goldman Sachs sees growth from investment banking.
Credit: www.fool.com
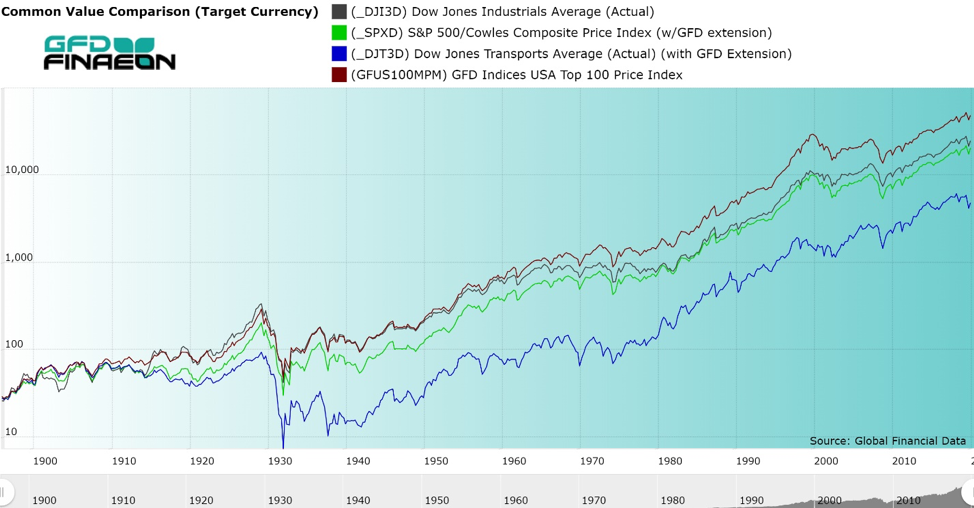
Historical Market Events
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) has seen countless historical market events. These events have shaped the index and affected investors globally. Understanding these events helps to grasp market dynamics better.
Market Crashes
The DJIA has experienced several significant market crashes. These crashes often led to widespread panic and economic downturns. Here are a few notable examples:
- 1929 Stock Market Crash: Known as Black Tuesday, the market lost nearly 12% in a single day. This crash led to the Great Depression.
- 1987 Black Monday: The market dropped over 22% in one day. It remains one of the largest single-day percentage drops in DJIA history.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: Triggered by the housing bubble burst, the DJIA lost over 50% from its peak.
- 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic: The market saw rapid declines as the pandemic spread. The DJIA fell by 37% in a matter of weeks.
Bull Markets
Conversely, the DJIA has also enjoyed numerous bull markets. During these periods, stock prices rise and investors gain confidence. Some remarkable bull markets include:
- Post-World War II Boom: The economy recovered and the DJIA soared. From 1949 to 1966, the market saw significant growth.
- 1982-2000 Bull Market: Often called the “Great Bull Market,” it was fueled by economic policies and technological advancements.
- 2009-2020 Bull Market: After the financial crisis, the DJIA saw a steady rise. This period marked one of the longest bull markets in history.
These historical market events illustrate the volatility and resilience of the DJIA. They highlight how external factors can dramatically impact the stock market. Understanding these events is crucial for any investor.
Investment Strategies
Comparing the Dow Jones Industrial Average with other indexes helps investors understand market trends. This can guide better investment strategies. Understanding these comparisons is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Investing in the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) requires a solid plan. Different strategies offer various approaches to profit. Some prefer a hands-off method. Others take a more involved route. Let’s explore these strategies.
Passive Investing
Passive investing in the DJIA means buying and holding stocks. This approach requires minimal trading. Investors rely on the market’s long-term growth. It involves less stress and fewer decisions. It can be cost-effective due to lower fees. This strategy suits those with a long-term focus.
Active Investing
Active investing involves frequent trading. Investors aim to beat the market’s average returns. It requires deep research and market analysis. This strategy can be more profitable. But it involves higher risks and costs. Active investors need to stay updated on market trends. This approach suits those who enjoy market analysis. “`
Future Projections
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) stands as a key indicator of economic health. Investors closely watch its movements to gauge future market conditions. Predictions about the DJIA help in planning investments and understanding potential market trends.
Economic Predictions
Experts often analyze various factors to make economic predictions about the DJIA. These factors include:
- GDP Growth
- Unemployment Rates
- Inflation Levels
For instance, higher GDP growth may indicate a rise in the DJIA. Conversely, high unemployment can lead to a drop. Inflation also plays a crucial role. Moderate inflation can boost the market, while high inflation can cause a decline. Understanding these elements helps in forecasting the DJIA’s future movements.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment refers to the overall attitude of investors towards the market. It can be either positive or negative and greatly impacts the DJIA. Here are some key aspects:
| Sentiment Type | Impact on DJIA |
|---|---|
| Bullish | Positive |
| Bearish | Negative |
When investors feel optimistic, the sentiment is bullish. This typically leads to a rise in the DJIA. On the other hand, a bearish sentiment, stemming from fear or uncertainty, can cause a decline. Market sentiment is influenced by various factors, including economic news, political events, and corporate earnings reports.
Keeping an eye on market sentiment helps in making informed decisions about the DJIA.
Credit: globalfinancialdata.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Dow Jones Industrial Average?
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a stock market index. It represents 30 prominent companies listed on U. S. stock exchanges.
How Is The Djia Calculated?
The DJIA is a price-weighted index. It is calculated by adding the prices of the 30 stocks and dividing by a divisor.
Why Is The Djia Important?
The DJIA is important because it indicates the overall health of the U. S. stock market. Investors use it to gauge market trends.
How Does The Djia Compare To The S&p 500?
The DJIA includes 30 large companies, while the S&P 500 includes 500. The S&P 500 is more diverse and comprehensive.
Conclusion
Understanding the Dow Jones Industrial Average is crucial for investors. It helps you track market trends. Comparing it with other indexes provides deeper insights. Use this knowledge to make informed decisions. Stay updated with market changes. This will improve your investment strategies.
The Dow Jones is a useful tool for financial planning. Stay informed and invest wisely.





