The Fascinating World of Ladybug Larvae: Nature’s Pest Control Heroes

Ladybug larvae are often overlooked but play a crucial role in the ecosystem. These small, predatory creatures are the early stage of the well-known ladybug and are essential for controlling pests like aphids in gardens and crops. Understanding ladybug larvae is key to appreciating their importance in natural pest management and their role in maintaining a balanced ecosystem.
Life Cycle of Ladybug Larvae
The life cycle of a ladybug is fascinating, with the larval stage being one of the most important phases. Ladybug larvae hatch from eggs laid by adult ladybugs and immediately begin their quest for food. This stage lasts for about two to three weeks, during which the larvae undergo several molts as they grow. Each molt brings them closer to their transformation into adult ladybugs. Understanding the life cycle of ladybug larvae helps gardeners and farmers to recognize and protect these beneficial insects during this vulnerable stage.
The Appearance of Ladybug Larvae
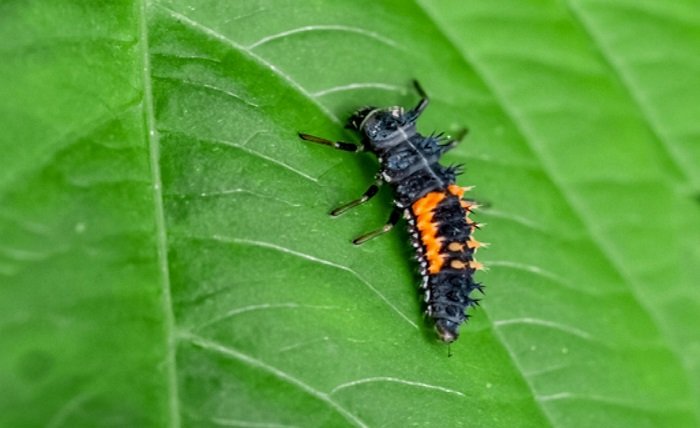
Ladybug larvae look quite different from the adult ladybugs we are familiar with. They have elongated, spiny bodies and are typically black with orange or yellow spots or markings. This distinctive appearance can make them easy to identify in the garden. However, many people mistake them for harmful pests, not realizing that these larvae are voracious predators of garden pests. Recognizing ladybug larvae is essential for gardeners who want to encourage natural pest control in their gardens.
Feeding Habits of Ladybug Larvae
The primary diet of ladybug larvae consists of aphids, which are among the most destructive pests for many plants. A single ladybug larva can consume hundreds of aphids during its development, making them an invaluable ally in the garden. In addition to aphids, ladybug larvae may also feed on other soft-bodied insects like mites and small caterpillars. Understanding the feeding habits of ladybug larvae can help gardeners and farmers make informed decisions about pest management, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
The Role of Ladybug Larvae in Natural Pest Control
Ladybug larvae are often referred to as nature’s pest control heroes. Their ability to consume large quantities of pests like aphids makes them a vital component of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies. By reducing the population of harmful insects, ladybug larvae help to maintain a healthy balance in the ecosystem. Encouraging the presence of ladybug larvae in gardens and farms can significantly reduce the need for synthetic pesticides, promoting a more sustainable approach to agriculture.
How to Attract Ladybug Larvae to Your Garden
Attracting ladybug larvae to your garden is a great way to enhance natural pest control. To do this, you can plant a variety of flowers and herbs that attract adult ladybugs, such as dill, fennel, and marigolds. Providing a source of water and avoiding the use of broad-spectrum insecticides will also help to create a welcoming environment for ladybug larvae. Additionally, allowing some aphids to remain in the garden can ensure a steady food supply for the larvae, encouraging them to stay and thrive.
The Importance of Ladybug Larvae in Agriculture
In agriculture, ladybug larvae are highly valued for their pest control abilities. Farmers often rely on these larvae to manage pest populations in crops without resorting to chemical pesticides. The presence of ladybug larvae can lead to healthier crops and increased yields by keeping harmful insect populations in check. Understanding the role of ladybug larvae in agriculture can help farmers adopt more sustainable practices, benefiting both the environment and their bottom line.
Common Misconceptions About Ladybug Larvae
Despite their beneficial role, ladybug larvae are often misunderstood. Some people mistakenly believe that these larvae are harmful pests themselves, leading to unnecessary eradication efforts. Others may not recognize them at all, missing the opportunity to harness their natural pest control abilities. By debunking common misconceptions about ladybug larvae, we can encourage more people to protect and support these important insects in their gardens and farms.
The Challenges Faced by Ladybug Larvae
Ladybug larvae, like many beneficial insects, face several challenges in the modern world. Habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change are all factors that can negatively impact their populations. Additionally, the introduction of non-native ladybug species can create competition for resources, further threatening native larvae. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing strategies to protect ladybug larvae and ensure their continued role in natural pest control.
Conclusion
Ladybug larvae are a small but mighty force in the natural world, playing a crucial role in controlling pest populations and maintaining a healthy ecosystem. By recognizing their importance and taking steps to support their presence, we can reduce our reliance on chemical pesticides and promote more sustainable gardening and farming practices. Whether in a small garden or a large farm, the presence of ladybug larvae is a sign of a thriving, balanced ecosystem.
FAQs
1. What do ladybug larvae eat? Ladybug larvae primarily eat aphids but also consume other soft-bodied insects like mites and small caterpillars.
2. How can I identify ladybug larvae in my garden? Ladybug larvae are black with orange or yellow spots, have elongated, spiny bodies, and look quite different from adult ladybugs.
3. Are ladybug larvae harmful to plants? No, ladybug larvae are beneficial to plants as they help control harmful pests like aphids, which can damage crops and garden plants.
4. How long does the ladybug larval stage last? The larval stage of a ladybug lasts about two to three weeks, during which the larvae undergo several molts before becoming adult ladybugs.
5. What can I do to attract ladybug larvae to my garden? Planting flowers and herbs that attract adult ladybugs, providing water, and avoiding broad-spectrum insecticides can help attract and support ladybug larvae in your garden.